Fig: JdbcExample1(ProjectArchitec).JPG
Low Level means it is specific to one type of dependent
persistence logic
Persistence Logic: is responsible for accessing persistence
Data
·
If I’m using low level persistence logic in Business Logic (i.e High
Level Logic) so I can not connect to all the Back end servers.
To avoid this
problem we have to use another layer , keep the persistence logic in a separate
object, that object is nothing but a
Data Access Object (DAO).
SO here DAO is
a Design Pattern, Design Pattern which gives a solution for a problem.
(Example: I’m
facing a problem, I will try to interact with a friend who is already faced the
problem because he will have ready made solution for that problem, no need to
waste my time to solve the problem, because already ready made solution (design
pattern) is available
Fig: DAO DesignPattern.JPG
·
When it comes into the project (enterprise application) we need to
concentrate in optimizing the code, making the more reusable, and also
testable.
·
The DAO is the most common pattern implemented into the enterprise
applications.
What is a Pattern?
·
Pattern is a three part document that describes the context
(situation), reoccurring problem and the best solution for the problem in the
given context (situation).
·
The software patterns are categorized into multiple type for
convenience in learning and applying.
·
The design patterns is one of the category. This lists the patterns
describing the problems related to design and development of the software
applications
THE DAO DESIGN PATTERN:
·
As the title describes this is a design pattern
Context (situation):
·
We want to create enterprise Application with reasonable business logic
having a requirement of accessing multiple (variety) of datastore and /or found
that may have a requirement of migrating from one type of data store (database)
to other. Easy to migrate between the different types of data stores. That is
in my application I want to connect to LDAP to take credentials, same
application I want to connect to File Systems to accept login details.
Problem:
·
We want to separate the low-level persistence (data access) logic from
Business Logic. But this so this solution leaves a problem that is how do you
separate in a best way? Thus this solution we kept in a problem.
Forces: (Why):
·
We want to have a proper
responsibility division that is:
(a) improves the quality of the system.
(b) reduces the cost and time for the
development
·
To enable unit testing, make the system more comfortable for testing.
·
Easy to migrate between the different types of data stores.
Solution:
·
Implement the low-level persistence logic into a separate object,
exposing the data access operations through high-level API to the service
layer.
What is DAO ?
Ans: DAO is a design pattern that describes separating
the low-level persistence logic from the business logic, implementing into a
separate (independent) object.
Note: this special object introduced implementing the DAO
pattern is also refered as a DAO i.e: Data Access Object
Fig: DAO DesignPattern.JPG
From this
discussion and the above architecture we understand JDBC is used for
implementing the DAO in Java for accessing the tabular data store
Implementing DAO Design Pattern in our project
Use Case
Diagram of EMPLOYEE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
Fig: DAO
DesignPattern1(a).JPG
Fig: DAO DesignPattern1.JPG
For Example:
Implementing
the Data Access Layer for ‘CreateEmployee’ use case of ‘Employee Management
System (EMS).
//EmployeeDAOI.java
package
com.st.ems.dao;
public
interface EmployeeDAOI
{
void save(int eno,String name, double sal, int
dno);
//we will
change this struture later
//we will add some more methods as we proceed
}
//EmployeeDAO.java
package
com.st.ems.dao.jdbc;
import
com.st.ems.dao.EmployeeDAOI;
import
java.sql.*;
import
java.util.*;
public class
EmployeeDAO implements EmployeeDAOI
{
public void save(int eno, String name,double
sal, int dno)
{
//this method is responsible for saving the
given details into emp table
//to do: execute the following SQL
String sql="insert into emp
values("+eno+",'"+name+",',"+sal+","+dno+")";
//how to execute?
//use JDBC
//Write this Connection con=null here only to
make visible to all the blocks
Connection con=null;//null is necessary whn u
r declaring as a local variable
try
{
//step 1.1
String
driverClassName="oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver";//here we are using
oracle driver
Class c=Class.forName(driverClassName);
Driver d=(Driver)c.newInstance();
//step 1.2
String jdbcUrl="jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:XE";
Properties p=new Properties();
p.put("user","system");
p.put("password","manager");
//Connection con=null;//i can not use con
ref variable in finally block as it is local to this
//block
con=d.connect(jdbcUrl,p);
//step2
Statement st=con.createStatement();
//step3
st.executeUpdate(sql);
}//end of try block
catch(Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
//to report the error, we will set run time
error
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
finally
{
try
{
//step 4:
con.close();
}//try
catch(Exception e){}
}//finally
}//save
}//class
/* now we are
writing Tese case for DAO object [that is save()] for this we have to use JUNIT
but
we are using
main() for this application
*/
//EmployeeDAOTestCase.java
import com.st.ems.dao.jdbc.EmployeeDAO;
import com.st.ems.dao.EmployeeDAOI;
public class EmployeeDAOTestCase
{
private
EmployeeDAOI edao;
public void
testsave()
{
edao.save(102,"e102",20000,20);
System.out.println("Details saved");
}
public static
void main(String s[])
{
EmployeeDAOTestCase test=new EmployeeDAOTestCase();
test.edao=new EmployeeDAO();
test.testsave();//here Driver object is created
//test.testsave();//here 2nd Driver object is
created but one Driver object is enought to handle
//multiple request from diffrent clients,
connections as it is a Thread -safe
}
}
/*
D:\material\java(E
DRIVE)\java\AdvJava\jdbc\DAO>javac -d . *.java
D:\material\java(E
DRIVE)\java\AdvJava\jdbc\DAO>D:\material\java(E
DRIVE)\java\AdvJava\jdbc\DAO>set
classpath=C:\oraclexe\app\or
acle\product\10.2.0\server\jdbc\lib\ojdbc14.jar;.;
D:\material\java(E
DRIVE)\java\AdvJava\jdbc\DAO>java EmployeeDAOTestCase
Details saved
*/
Fig: DesignPattern2.JPG
Q: is our DAO created efficient?
Ans: No, we
need to multiple changes. Let us look into all of them one after the other
·
In the EmployeeDAO created earlier the save() method is programmed to
create a new instance (object) of Driver class on every request, which is not
effective.
·
Considering the following points with respect to the Driver:
(1)
The Driver object is Thread-safe
means Driver object performs consistently even on concurrent requests from
multiple threads
(2)
A single instance of Driver can be used to
create multiple connections because it is Thread-safe.
If we create the multiple instances of Driver class, unnecessarly garbage is
stored into the memory, and performance becomes slow.
(3)
Considering these points a single instance of
Driver is enough for an application per data base.
Fig: FactoryClass(EmpDao.JPG
(INTRODUCTION TO DRIVER MANAGER)
·
That means we want to redesign the DAO such that it should work with
single instance of Driver class irrespective of the number of clients and
requests.
·
To address this requirements JDBC introduces DriverManager class
Q: What is Driver Manager class?
The
java.sql.DriverManager is a factory class that is designed to create the
Connection Managing the Driver objects.
Why DriverManager?
Ans: to centralize the code(
means connect() method) creating the Connection using the Driver object. So
that we can avoid multiple instances (objects) of a Driver class to create.
Here the code means connect() method.
Q: How
DriverManager functions?
We know that the basic
functionality of the DriverManager is to create the Connection managing the
Driver object. The getConnection() method will create connection using
registered Driver object.
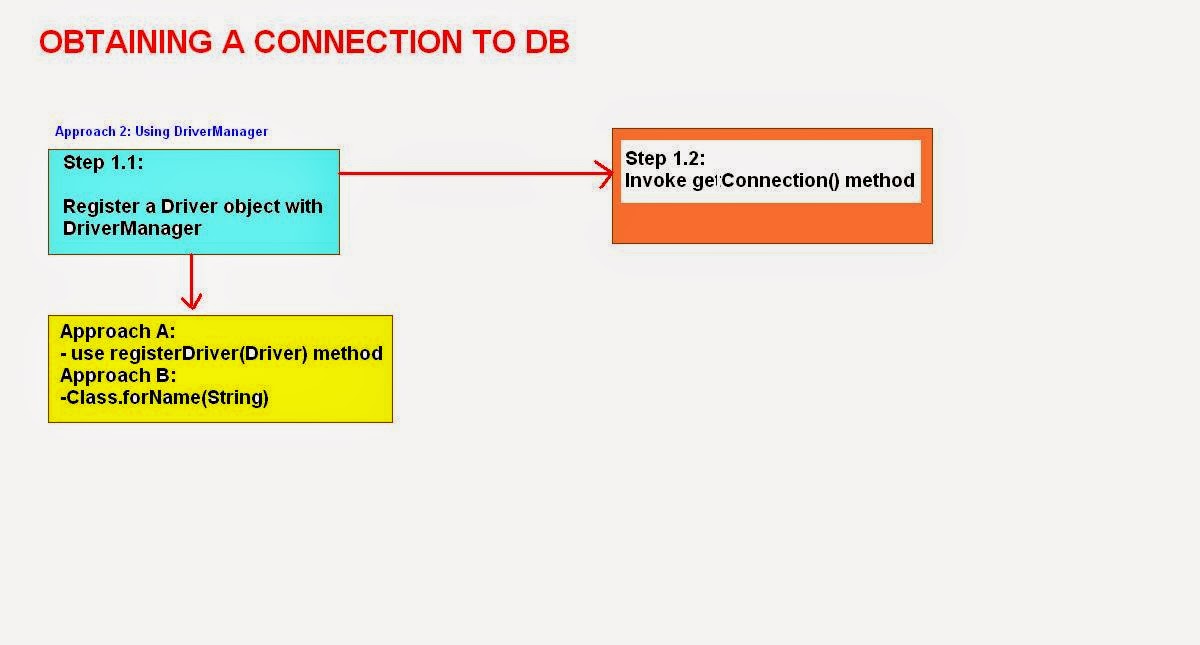
Working with
DriverManager
Fig: DriverManager
FactoryClass(.JPG
The following two steps are
involved in doing this:
Step1: Register the Driver to
DriverManager
Step2: Invoke the getConnection()
to get the Connection
Step1: Register the Driver to DriverManager
·
The following static method of DriverManager is
used to do this: registerDriver(Driver
d);
·
We want to do this only once for each driver to
use in the application.
·
The jdbc specification includes a rule to have a
static block in the Driver implementation class that should create an object if
itself and register it to the DriverManager.
Example: the following snippet shows the code of
OracleDriver class.
//it is a internal code (readymade ), just we are writing to
awareness only, we have to use not to write)
public class OracleDriver implements Driver
{
Static
{
DriverManager.registerDriver(new OracleDriver());
}
--
--
}
·
From this discussion we understand if we can
load the driver class into the JVM it
results to execute the static block of the same class which registers this
driver object to DriverManager.
public class ClassLoadTest {
public static void main(String
args) throws Exception
{
System.out.println("In main
method");
}
}
class Test1
{
static
{
System.out.println("Test1
static block");
}
}
Output:
In main method
Ex2:
public class ClassLoadTest {
public static void main(String
args[]) throws Exception
{
System.out.println("In main
method");
for(int
i=0;i<10;i++)
{
Class.forName("Test1");
}
}
}
class Test1
{
static
{
System.out.println("Test1
static block");
}
}
In Main method
Test1 static block
0
1
.
10
Note:
Class c=Test1.class ;//for dynamic we can not use this
Class c=Class.forName(Test1); both are same to load the
class into JVM , when you know about the class name go for Class
c=Test1.class;//it is implicit field like super, this, class
The following 3 points are important to consider with respect
to class loading:
1.
static
block executing all the time of loading the class into JVM. Note: this is not
true always in some jvm’s the static blocks are delayed to execute on first
access to any member of the class.
Example:
public class ClassLoadTest {
public static void main(String
args[]) throws Exception
{
System.out.println("In main
method");
/*for(int
i=0;i<10;i++)
{
Class.forName("Test1");
}*/
Class
c=Test1.class;
System.out.println("c");
System.out.println("Test1 is
loaded");
System.in.read();//waits until
user press enter
System.out.println("Count
:="+Test1.count);
}
}
class Test1
{
static int count=10;
static
{
System.out.println("Test1 static
block");
}
}
In main method
c
Test1 is loaded
Test1 static block
Count :=10
2.
A class is loaded into the jvm on first access
to any member of class , this is implicit (or)
·
Use class.forName(-); //this is explicit
·
Use ‘class’ implicit field
3.
Invoking
the class.forName(-); with the same input for multiple times will not
result loading class for multiple times.
Step 1.2: invoking the getConnection() method:
·
After we register the driver to DriverManager we
can use any of the following static
methods of DriverManager to get the Connection.
Connection
getConnection(String url, Properties jdbcprops) throws SQLException
·
This method finds the registered drivers that
can use the given url for getting the connection. If found use it to get the
connection. Otherwise throw SQLException ‘No suitable Driver Found’
·
This method is just a convenience method. This
method internally creates the properties object setting the given username and
password, and invoke above method.
Connection
getConnection(String url, String db_user, String db_password) throws SQLException
·
This is also a convenience useful in case if
there are to no properties describe for getting the Connection
Fig: Approach2DriverManager.JPG



.JPG)




.JPG)
a.JPG)
b.JPG)
.JPG)